2023년 대학생 인턴 S/W역량테스트 준비
알고리즘 공부 - 삼성에서 자주 출제하는 유형
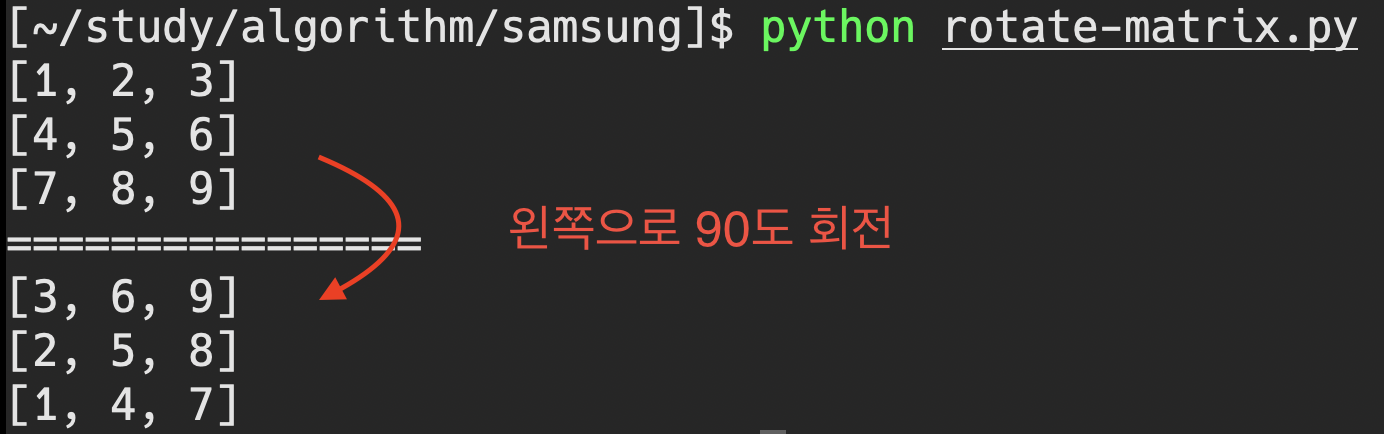
행렬 회전
def rotate_left(mat):
'''
행렬을 반시계방향으로 90도 회전
mat -> result
0 1 2
0|1 2 3 3 6 9
1|4 5 6 2 5 8
2|7 8 9 1 4 7
'''
n = len(mat)
result = [[0]*n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
result[i][j] = mat[j][n-1-i]
return result
결과
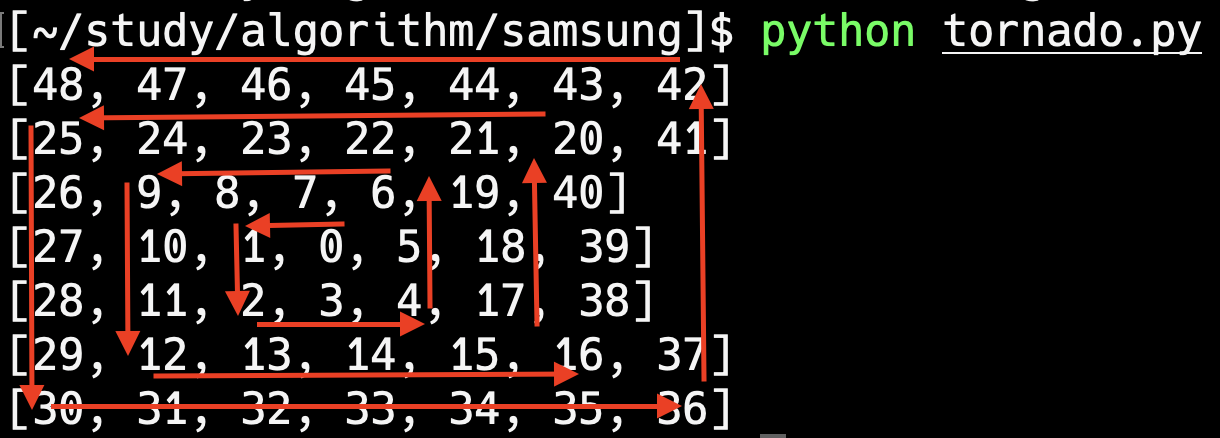
회오리 모양으로 이동
move_count distance_count 사용
def move1(_map):
'''
_map - 토네이도가 지나갈 길이가 홀수인 2차원 정사각 리스트
'''
dx, dy = [0, 1, 0, -1], [-1, 0, 1, 0]
n = len(_map)
mark = 1
# states
distance, direction = 1, 0 # 이동 거리와 방향
move_count, distance_count = 0, 0 # 한 번 이동 횟수, 한 칸 이동 횟수
x = y = int(n/2)
while True:
# 이동
x, y = x + dx[direction], y + dy[direction]
distance_count += 1
# 종료 조건
if x == 0 and y == -1:
return
# distance 만큼 이동한 뒤 방향 전환, move_count 증가
if distance_count == distance:
direction = (direction+1)%4
distance_count = 0
move_count += 1
# 두 번 이동 후 distance 증가
if move_count == 2:
move_count = 0
distance += 1
_map[x][y] = mark
mark += 1
for loop 사용
def move2(_map):
'''
for loop 사용
아래의 이동을 두 번 반복
distance만큼 한 번 이동하고 direction 전환
distance 증가
'''
dx, dy = [0, 1, 0, -1], [-1, 0, 1, 0]
n = len(_map)
x = y = int(n/2)
mark = 0
direction, distance = 0, 1
while True:
for _ in range(2):
for _ in range(distance):
x, y = x + dx[direction], y + dy[direction]
mark += 1
if x == 0 and y == -1:
return
_map[x][y] = mark
direction = (direction+1)%4
distance += 1
결과

Comments